Metadata SEO sounds technical, but it is really about how your pages present themselves to search engines and real people at the same time. Things like title tags and meta descriptions are not just small bits of code. They shape how your page shows up in search results, how clear your message is, and whether someone chooses your link over five others.
A lot of websites lose traffic not because their service is bad, but because their metadata is messy, vague, or written without strategy. When done right, metadata helps search engines understand your page and helps users quickly see that you have exactly what they are looking for. That combination is where better visibility and more clicks usually start.
Let’s Start Simple: What Is Metadata in SEO?
Metadata in SEO is the information that describes your web page rather than the visible content on it. It lives in the code, but its job is very human. It tells search engines what your page is about and helps people decide whether your result is worth clicking. In a way, metadata works as a bridge between your website and the outside world. Before anyone reads a single paragraph on your page, metadata is already shaping how that page is understood and presented.
The two pieces most people know are the title tag and the meta description. When you search on Google and see a blue headline and a short summary under it, that is metadata at work. But metadata goes beyond that. It includes technical instructions, indexing rules, language signals, canonical hints, and other behind-the-scenes details that guide how search engines crawl, interpret, and store your pages. Some of it is about visibility, some of it is about control, and some of it is about keeping your site organized at scale.
Think of metadata as the label on a box. The content is what is inside. Metadata is what says what is inside, who it is for, and how it should be handled. If the label is clear and accurate, the right people find the box, open it, and get what they expected. If the label is missing or confusing, the box gets ignored, misplaced, or misunderstood. Without good labels, even great content can sit unseen, not because it lacks value, but because no one could clearly tell what it offered.
How We Approach Metadata SEO at Lengreo
When we at Lengreo, work on metadata SEO, we do not treat it like a tiny technical checkbox. For us, metadata sits right between strategy and performance. Titles and descriptions are not written in isolation. We connect them to search intent, to the actual content on the page, and to what the business is trying to achieve. If a page is meant to drive leads, the metadata should reflect that purpose clearly. If it is educational, the snippet should feel helpful and specific, not generic. We look at how each page appears in search results and ask a simple question – would we click this over the others?
Because we work with B2B, tech, and service driven companies, scale matters too. We build metadata systems, not just single lines of text. That means clear structures for service pages, content clusters, and landing pages, so search engines understand the site architecture and users see consistent, relevant messaging. At the same time, we keep a close eye on performance data like CTR and engagement to refine metadata over time. For us, metadata SEO is not decoration. It is part of how we turn visibility into real business opportunities.
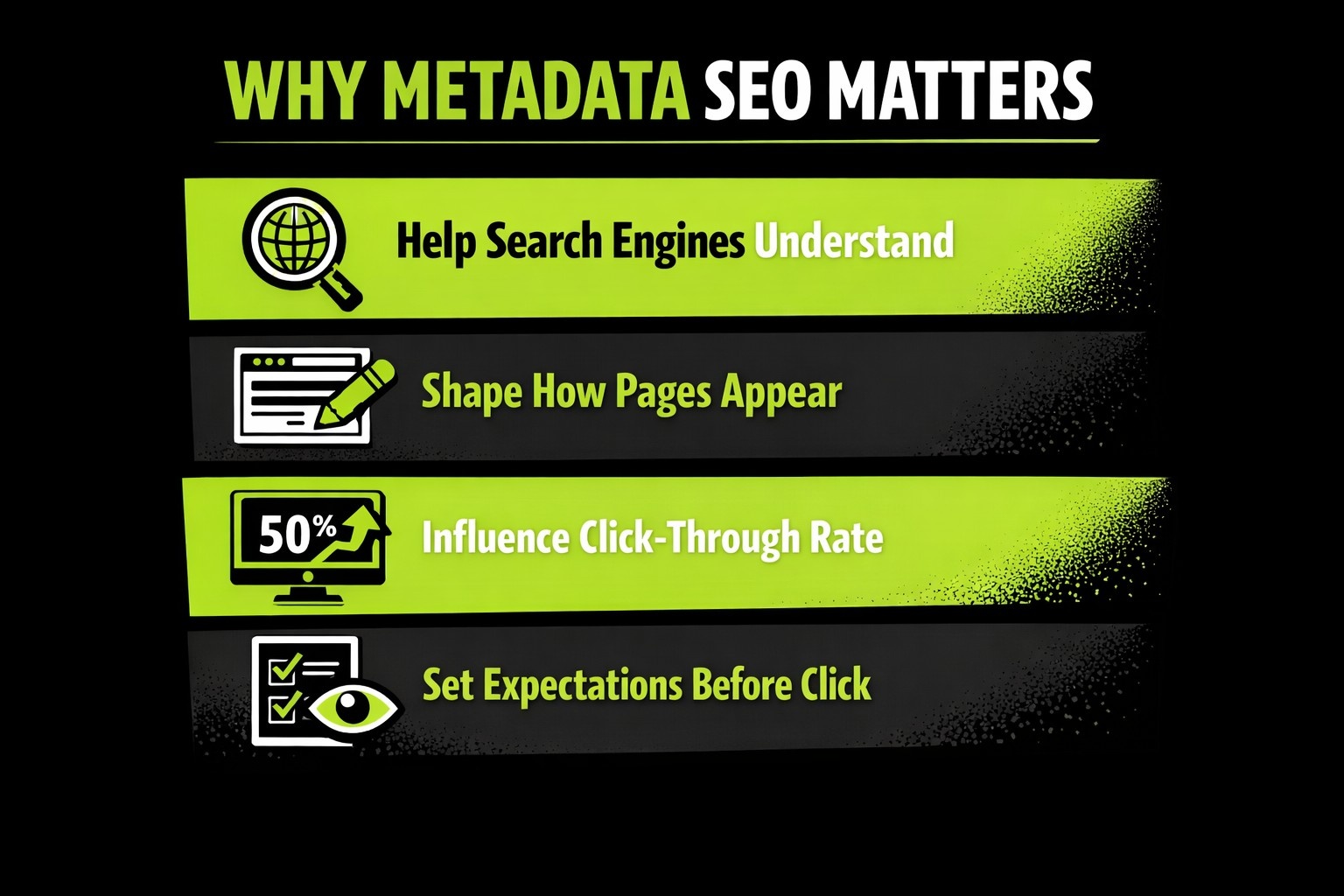
Why Metadata SEO Matters
Metadata often feels small compared to content or backlinks, but it plays a surprisingly big role in how your pages perform. Here is why.
1. They Help Search Engines Understand Page Purpose
Search engines are constantly trying to answer one core question: what is this page really about? Metadata gives them an early and structured answer. The title tag frames the topic, supporting tags reinforce context, and together they reduce ambiguity.
When metadata clearly matches the content, search engines do not have to guess. That clarity helps pages get grouped correctly, matched with the right queries, and compared more accurately against competing results.
2. Shape How Your Pages Appear in Search Results
Metadata controls how your page is presented in search results. This is your first impression.
Title tags and meta descriptions:
- Form the headline and summary in most search results
- Influence how professional and relevant your result looks
- Help your page stand out among competitors
You might have the best guide on a topic, but if your snippet looks vague or messy, people scroll past.
3. Influence Click-Through Rate (CTR)
Ranking gets you seen. Metadata helps you get chosen. Two pages can sit side by side in search results, but the one with clearer, more specific metadata often earns more clicks. Strong titles and descriptions turn impressions into visits.
More Traffic Without Extra Rankings
When your snippet is more relevant and compelling, a higher percentage of people click your result. You gain additional traffic even if your position in search results does not change.
Better Engagement Signals
Users who click because the metadata accurately reflects their intent are more likely to stay, read, and interact. That alignment often leads to lower bounce rates and stronger on-page behavior.
Stronger Overall Performance From the Same Page
Improved CTR and engagement mean the same piece of content delivers more value over time. Instead of constantly creating new pages, you get more out of the one you already have.
4. They Set Expectations Before the Click
Metadata quietly makes a promise. It tells users what kind of page they are about to land on. If the page delivers on that promise, users stay longer and engage more. If it does not, they leave quickly.
That alignment between snippet and real content is where trust begins. Consistent expectations reduce frustration, improve engagement, and help build credibility with both users and search engines.
5. They Prevent Indexing and Crawling Issues
Not all metadata is about visibility. Some of it is about control.
Search engines need guidance on what to index, what to skip, and which versions of a page matter most. Without proper directives, low value pages, duplicates, or internal system pages can slip into the index and dilute overall site quality. Metadata acts as traffic control for crawlers, steering them toward pages that deserve attention.
6. They Support Large-Scale SEO Management
On bigger sites, metadata becomes a system, not just a line of text.
When handled properly, metadata:
- Keeps thousands of pages structured consistently
- Helps automate SEO rules at scale
- Supports category, product, and content templates
It is one of the few SEO elements that can be standardized without killing quality.
7. They Act as a Quality Signal
Metadata that is clear, specific, and aligned with content signals that the page is well maintained.
Search engines see:
- Unique titles
- Descriptions that reflect real content
- Clean technical directives
All of this contributes to the overall quality profile of your site.
What Metadata Does for Search Engines and Users
Metadata operates in two directions at once. It helps machines interpret your page and helps people decide whether it is worth their time. The same elements serve both sides, just in different ways.
For Search Engines, Metadata:
- Provides structured clues about topic and purpose
- Supports indexing and ranking decisions
- Helps categorize and cluster content
For Users, Metadata:
Metadata shapes the moment of choice. The title and description form a quick summary that helps people judge relevance in seconds. Clear, accurate snippets reduce uncertainty, set expectations, and make it easier for users to pick the result that best matches what they are looking for.
In short, metadata connects intent with content. It helps the right person land on the right page.
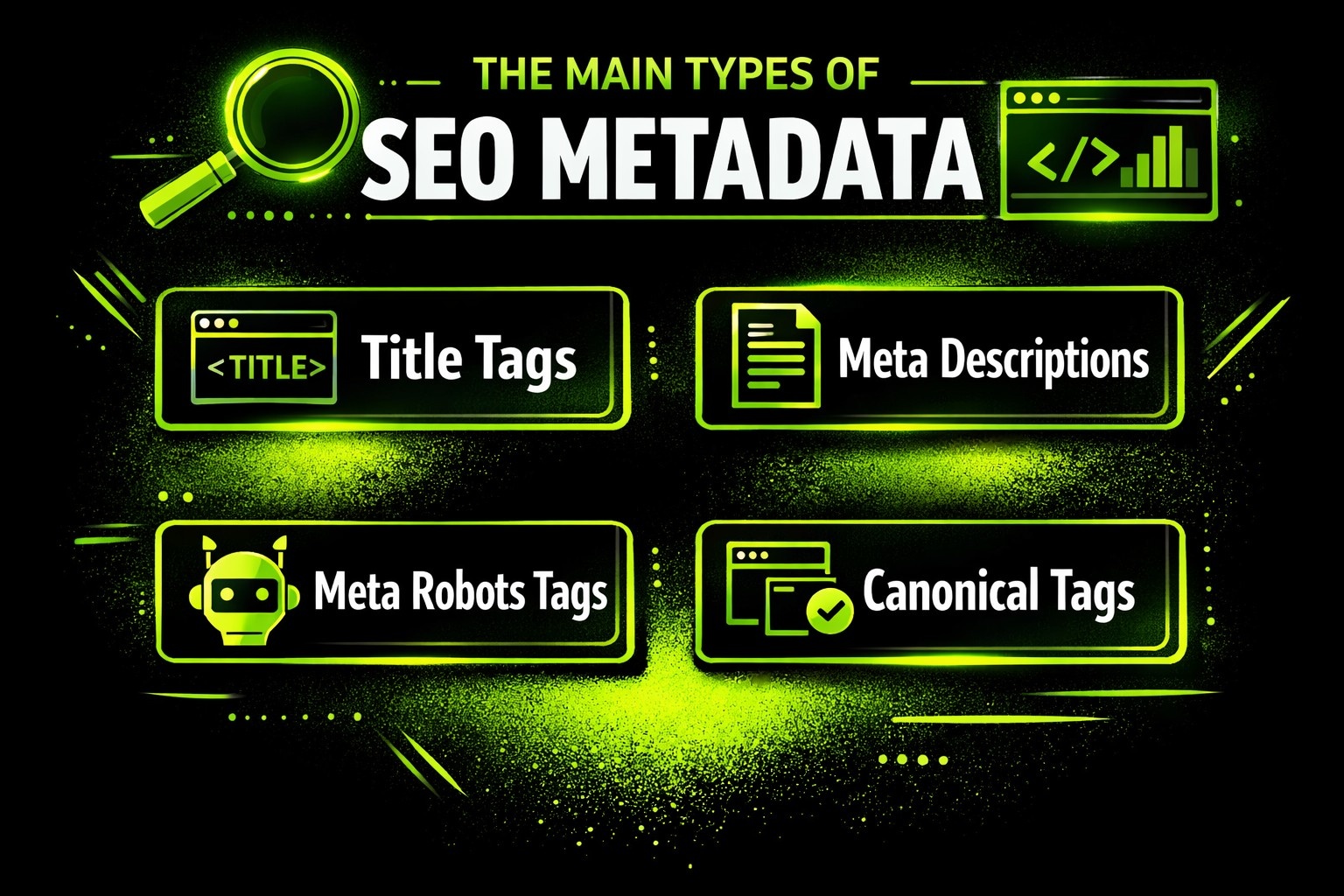
The Main Types of SEO Metadata
Not all metadata serves the same function. Some elements shape visibility in search results, others guide technical behavior, and some exist mainly to support usability and targeting. Together, they create the structural layer that helps search engines interpret your site correctly.
Title Tags
- Define the main topic of the page
- Act as a primary relevance signal for search engines
- Form the clickable headline in search results
- Strongly influence click-through rate
Title tags sit at the intersection of ranking and user choice, which makes them one of the most important metadata elements.
Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions work more on persuasion than on ranking. They summarize the page and help users understand what they will get before clicking. When written clearly and aligned with intent, they increase the likelihood that your result is chosen over others nearby in search listings.
Meta Robots Tags
- Control whether a page can be indexed
- Decide if links on the page should be followed
- Help keep low-value or internal pages out of search
- Guide crawlers toward important content
These tags function like instructions rather than marketing text. They shape how search engines handle your pages behind the scenes.
Canonical Tags
Canonical tags exist to solve duplication. When similar or identical pages appear under different URLs, this tag points search engines to the preferred version. It helps consolidate ranking signals and prevents pages from competing with each other internally.
Language and Hreflang Tags
Language Targeting
These signals tell search engines which language a page is written in, helping match users with content they can actually read.
Regional Targeting
Hreflang tags also handle regional variations, such as different versions of the same content for different countries.
- Prevent users from landing on the wrong country-specific version
- Help search engines serve geographically relevant content
- Reduce internal competition between regional pages
Avoiding Мismatches
They reduce the risk of users landing on the wrong language or regional page, improving both usability and relevance signals.
Each one plays a different role. Together, they form the framework that supports how your site is interpreted.
Metadata During Site Launch, Redesign, and Ongoing Optimization
Metadata becomes especially critical during site launches and redesigns, but its role does not end once the site is live. These moments are high risk for visibility, and they are also key opportunities to improve performance.
During Site Launch or Redesign
Site launches and redesigns are high risk moments for metadata.
When launching or relaunching, metadata helps:
- Preserve existing rankings
- Ensure important pages are indexable
- Avoid accidental noindex tags
- Maintain consistent title and description structures
A missing or misconfigured tag can quietly tank visibility. Metadata should be part of every launch checklist.
Metadata Optimization for Existing Pages
Metadata work does not stop after launch.
Over time, you should revisit pages to:
- Improve titles that are too generic
- Update descriptions to reflect new content
- Align metadata with updated keyword targets
- Fix duplication across pages
Small improvements here can lead to noticeable traffic gains without rewriting entire articles.
Why Metadata SEO Is a Long-Term Asset, Not a One-Time Task
Metadata is not a set-and-forget element of your site. It behaves more like living infrastructure that needs to evolve along with your business, your audience, and search behavior itself. The way people search today will not look exactly the same a year from now. New terms appear, priorities shift, and the language your customers use slowly changes. If your titles and descriptions stay frozen in time, they slowly drift away from what real users are looking for.
Your own business does not stay static either. Services expand, positioning becomes clearer, new markets open up, and old pages get updated or replaced. Metadata has to reflect those changes. When a service page is improved or repurposed, its title and description should be adjusted so search engines and users get the right message. Otherwise, you end up with pages that technically exist, but communicate outdated value in search results.
Metadata also supports long-term technical health. As websites grow, new pages are added, sections are restructured, and content gets archived. Without periodic checks, you can end up with duplicate titles, missing descriptions, incorrect noindex tags, or inconsistent canonical signals. These issues do not always cause sudden drops, but they quietly limit how efficiently search engines understand and prioritize your site.
Treating metadata as an ongoing process keeps your snippets aligned with search intent, opens the door to new keyword opportunities, and helps maintain strong click-through rates over time. It becomes part of regular site maintenance, just like updating content or improving performance. When handled this way, metadata SEO turns into a long-term asset that steadily supports visibility, traffic, and growth, instead of a one-time technical task that gets forgotten after launch.
Wrapping It Up
Metadata SEO may look like a background detail, but it plays a frontline role in how your pages are found, understood, and chosen.
It helps search engines interpret your content correctly. It helps users decide to trust your result. It supports technical control and large scale structure. And it quietly improves performance across your site.
If content is the story, metadata is the headline, the summary, and the instructions attached to it. Ignore it, and even strong pages can struggle. Get it right, and you give every page a clearer path to visibility and clicks.